Why Algo Trading is Becoming Essential in the Financial Markets
1. Speed and Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of algorithmic trading is speed. Algorithms can execute orders in milliseconds, responding to market conditions and price changes far quicker than any human could. This real-time responsiveness is especially important in highly volatile markets where prices can change rapidly.
2. Reduced Human Error
Humans are prone to mistakes, particularly when handling complex tasks under pressure. Algo trading eliminates human error by automating the decision-making process and ensuring that trades are executed based on predefined rules. This leads to greater accuracy and consistency in trading operations.
3. Backtesting and Strategy Optimization
Before implementing a trading strategy in a live market, backtesting allows traders to simulate trades based on historical data. Algo trading systems make it easy to test different strategies using historical data, enabling traders to fine-tune their models and improve the probability of success in real-world conditions.
4. Market Liquidity
Algorithmic trading plays a crucial role in providing liquidity to financial markets. By executing a high volume of orders, algo trading systems help ensure that assets are bought and sold efficiently, leading to more liquid markets with tighter bid-ask spreads.
5. Cost Savings
Algo trading reduces costs by automating trading processes that would otherwise require human intervention. Transaction costs and fees can be minimized through high-frequency, low-cost trades that algorithms execute swiftly and with minimal slippage.
Types of Algorithmic Trading Strategies
1. Trend-Following Strategies
Trend-following strategies rely on algorithms that identify and follow trends in the market. These algorithms look for patterns and execute trades based on price movements in a specific direction. Common trend-following strategies include:
- Moving Average Crossovers
- Momentum-Based Strategies
- Breakout Strategies
2. Mean Reversion
Mean reversion strategies are based on the idea that asset prices will eventually return to their average or "mean" after deviating for a period. Algorithms executing this strategy will buy when the price is below the mean and sell when the price is above it. These strategies work well in markets that fluctuate within a range.
3. Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage trading aims to exploit price differences between two or more markets. Algo trading systems can detect these price discrepancies and make trades to profit from them. Statistical arbitrage is a common type, which involves identifying statistical relationships between asset prices to execute arbitrage opportunities.
4. Market Making
Market-making algorithms provide liquidity to markets by simultaneously offering buy and sell orders. The algorithm profits by capturing the spread between the buying and selling prices. This strategy is commonly used by high-frequency trading (HFT) firms.
5. High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
High-frequency trading is a subset of algo trading that involves executing a high volume of orders within extremely short timeframes, often milliseconds or microseconds. HFT strategies rely on advanced technology and low-latency trading systems to capitalize on small price movements across multiple markets.
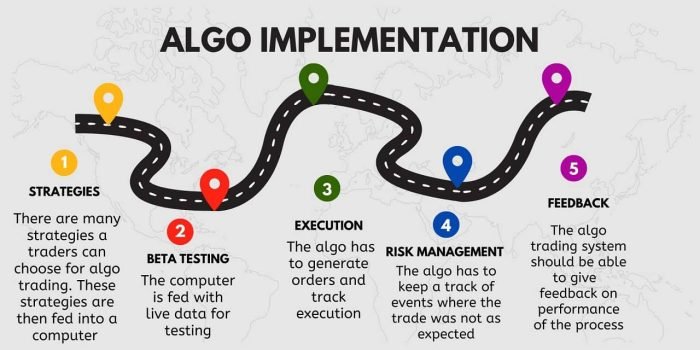
Key Components of an Algorithmic Trading System
1. Data Feed
Accurate, real-time market data is critical for algorithmic trading. The system must receive continuous data on price, volume, and market conditions to make real-time decisions.
2. Trading Algorithms
The core of an algo trading system is the algorithm itself, which processes incoming market data and uses mathematical models to make buy and sell decisions. These algorithms are designed to follow predefined rules that align with specific trading strategies.
3. Execution System
Once the algorithm makes a decision, the execution system sends the trade orders to the relevant exchanges or trading platforms. The system ensures that the orders are filled at the desired price levels and minimizes execution delays.
4. Risk Management
Effective risk management is a key component of any algo trading system. This includes setting stop-loss limits, managing position sizes, and using diversification to minimize exposure to any single asset or market event.
5. Backtesting Engine
Backtesting is essential to validate the performance of the trading algorithm. A backtesting engine allows traders to simulate the algorithm’s performance using historical data to assess its potential profitability and risk.
6. Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous monitoring of trading performance is necessary to ensure the algorithm is executing properly and making profitable decisions. Real-time reporting provides insights into trade executions, profit/loss, and the overall health of the strategy.